1. Introduction to AutoCAD

A landmark innovation in digital technology, AutoCAD has transformed how we create, build, and understand the physical world. This module begins with a thorough introduction to AutoCAD, delving into its definition and purpose, and taking you through its compelling history. We will also discover who utilizes this tool and how it has grown to become an industry-standard in many fields.
As we delve deeper, we’ll navigate the evolution of AutoCAD, tracing its lineage from the initial versions to its most contemporary incarnations. This includes exploring the differences and benefits of using AutoCAD for Windows versus AutoCAD for Mac, and contrasting the full version with AutoCAD LT. We will also touch on the unique advantages of the AutoCAD mobile app. Afterward, we’ll plunge into the significant impact AutoCAD has had across diverse industries, from its critical role in construction to its unexpected, yet substantial influence in the fashion industry. We’ll examine how AutoCAD has reshaped mechanical engineering, contributed to aerospace advancements, and even changed the face of interior design. The journey will continue with a detailed comparison between AutoCAD and other CAD software, including SolidWorks, Revit, and SketchUp, delving into their similarities, differences, user interfaces, and the value they each offer. Buckle up for an enlightening journey into the world of AutoCAD.
1. Introduction to AutoCAD
1.1. What is AutoCAD?
1.1.1. Definition of AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a computer-aided design (CAD) software developed and marketed by Autodesk. It is widely used in various industries for creating 2D and 3D designs, drafting, and modeling. AutoCAD provides a comprehensive set of tools and features that enable users to create precise and detailed drawings.
1.1.2. Brief History of AutoCAD
AutoCAD was first released in 1982 as a desktop application, making it one of the oldest and most established CAD programs. Over the years, AutoCAD has evolved and introduced new capabilities, becoming the industry standard for computer-aided design. It has undergone several major releases, each introducing enhancements and improvements to the software’s functionality.
1.1.3. The Purpose of AutoCAD
The primary purpose of AutoCAD is to facilitate the creation, modification, and documentation of designs. It provides a platform for architects, engineers, drafters, and other professionals to develop precise drawings that can be used for construction, manufacturing, and visualization purposes. AutoCAD offers a wide range of tools and functionalities that streamline the design process and enhance productivity.
1.1.4. Who Uses AutoCAD?
AutoCAD is used by professionals across various industries, including architecture, engineering, construction, product design, and manufacturing. Here are some examples of how different professionals utilize AutoCAD:
- Architects: Architects use AutoCAD to create detailed floor plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models of buildings. It helps them visualize and communicate their design ideas effectively.
- Engineers: Mechanical, electrical, civil, and structural engineers use AutoCAD to design and analyze components, systems, and structures. It enables them to produce accurate drawings and perform simulations.
- Drafters: Drafters use AutoCAD to transform rough sketches and concepts into precise technical drawings. They can create detailed drawings of mechanical parts, electrical circuits, piping systems, and more.
- Manufacturers: AutoCAD is widely used in manufacturing industries to design and produce parts, assemblies, and products. It helps manufacturers optimize their processes and ensure accurate production.
1.2. Different Versions of AutoCAD
AutoCAD offers various versions and editions to cater to different user requirements and platforms. Let’s explore some of the different versions and editions of AutoCAD:
1.2.1. The Evolution of AutoCAD: An Overview of Different Versions
AutoCAD has gone through several versions, each introducing new features and enhancements. Some notable versions include AutoCAD R12, AutoCAD 2000, AutoCAD 2010, AutoCAD 2015, AutoCAD 2020, and the most recent version, AutoCAD 2024. With each new release, AutoCAD has improved its performance, added more advanced tools, and expanded its compatibility with other software and file formats.
1.2.2. AutoCAD for Windows vs. AutoCAD for Mac
AutoCAD is available for both Windows and Mac operating systems. While the core functionality and features remain the same, there are some minor differences between the Windows and Mac versions. The user interface may have slight variations, and certain commands or functions may have platform-specific implementations. However, the overall workflow and capabilities of AutoCAD on both platforms are quite similar.
1.2.3. Full Version vs. AutoCAD LT
AutoCAD comes in two primary editions: the full version and AutoCAD LT. The full version of AutoCAD provides a comprehensive set of tools and functionalities for professional users, including 3D modeling, advanced customization options, and programming capabilities. AutoCAD LT, on the other hand, offers a more streamlined and cost-effective solution with limited features, primarily focused on 2D drafting and documentation. AutoCAD LT is suitable for users who primarily work with 2D drawings and do not require the advanced capabilities of the full version.
1.2.4. AutoCAD Mobile App
AutoCAD Mobile App is a companion application that allows you to access and edit your AutoCAD drawings on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. It provides a simplified interface and essential drawing tools, enabling you to view, annotate, and make changes to your drawings while on the go. The AutoCAD Mobile App supports seamless integration with the desktop version, allowing you to synchronize your files and work interchangeably between different devices.
Understanding the different versions and editions of AutoCAD helps you choose the most suitable option based on your requirements and platform preferences. In the next section, we will explore some essential concepts and techniques for creating and editing drawings in AutoCAD.
1.3. Significance of AutoCAD in Various Industries
AutoCAD, a computer-aided design (CAD) software, has revolutionized numerous industries by providing efficient and accurate design and drafting solutions. Its versatility and powerful features have made it an indispensable tool across various sectors. In this chapter, we will explore the significance of AutoCAD in different industries and understand how it has transformed the way professionals work.
1.3.1. Role of AutoCAD in the Construction Industry
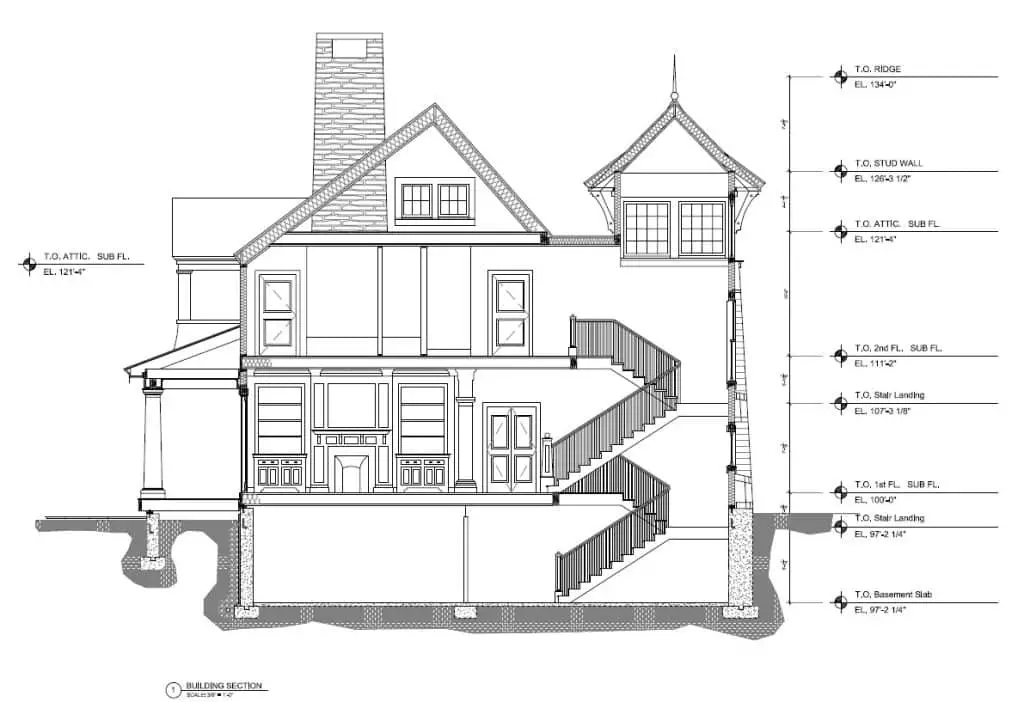
The construction industry heavily relies on AutoCAD for its design and documentation needs. AutoCAD enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create detailed 2D and 3D models of buildings, structures, and infrastructure projects. With AutoCAD’s precise measurement tools and intelligent objects, designers can accurately visualize their concepts and communicate them effectively to stakeholders.
AutoCAD’s drafting capabilities allow professionals to generate construction drawings, plans, sections, and elevations with ease. The software also facilitates the integration of various design disciplines, such as structural, electrical, and mechanical, into a cohesive model, enabling better coordination and collaboration among project teams.
1.3.2. Influence of AutoCAD in Mechanical Engineering
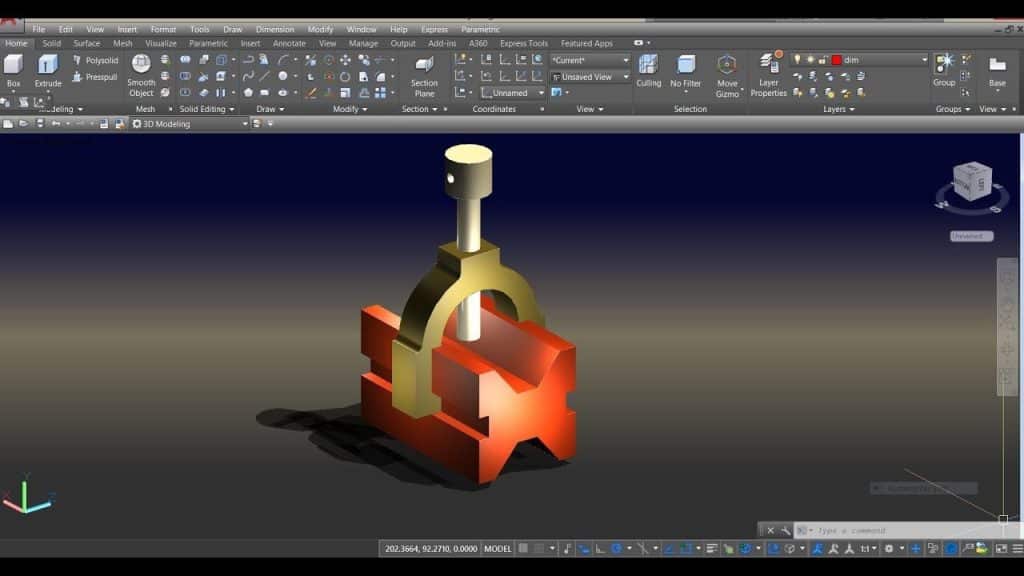
In the field of mechanical engineering, AutoCAD plays a crucial role in product design and manufacturing. Engineers leverage AutoCAD’s parametric modeling features to create 3D models of machine components, assemblies, and complex mechanisms. The software’s simulation capabilities enable them to test and analyze the behavior of designs under different conditions, leading to improved product performance and reliability.
AutoCAD’s integration with computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software allows engineers to generate machine code and CNC toolpaths directly from their designs. This seamless workflow enhances productivity and reduces errors in the manufacturing process.
1.3.3. Importance of AutoCAD in the Fashion Industry
AutoCAD has found its place in the fashion industry as well. Fashion designers utilize the software to create digital sketches and technical drawings of garments, footwear, and accessories. AutoCAD’s precise drafting tools enable designers to capture intricate details, patterns, and measurements accurately.

With AutoCAD, designers can experiment with different color schemes, fabrics, and textures virtually, saving time and resources in the design iteration process. The software also facilitates pattern making and grading, aiding in the efficient production of clothing and ensuring accurate sizing and fit.
1.3.4. AutoCAD’s Contribution to the Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry heavily relies on AutoCAD for the design and manufacturing of aircraft and spacecraft. Engineers use AutoCAD’s 3D modeling capabilities to create detailed digital prototypes of aerospace components, such as fuselages, wings, and engine assemblies. These models enable engineers to simulate and analyze the structural integrity, aerodynamics, and performance of the designs before physical production.
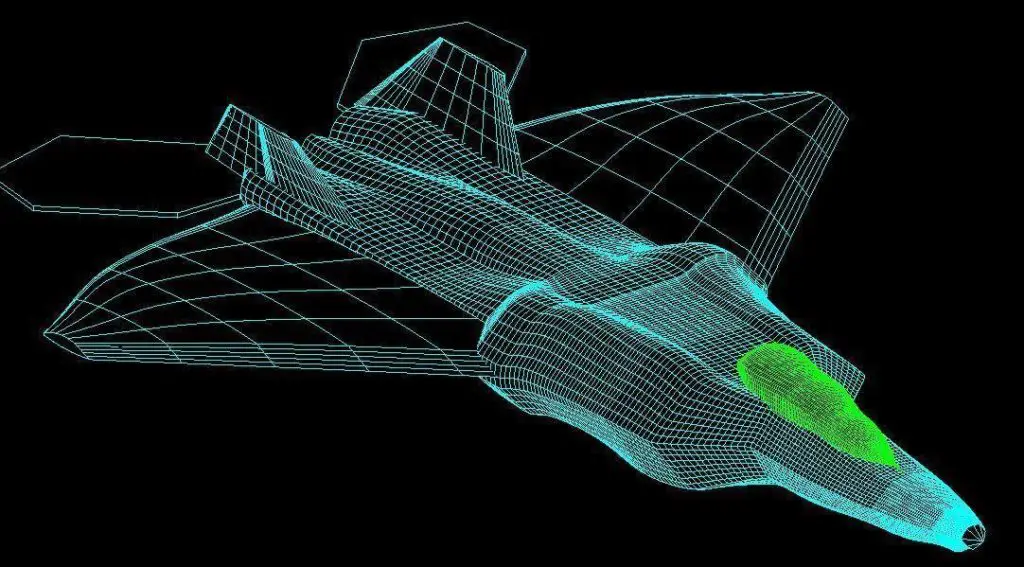
AutoCAD’s collaboration features allow aerospace professionals to work together on complex projects, ensuring seamless integration of different subsystems and reducing errors in the overall design. Additionally, the software’s documentation tools aid in the creation of manufacturing drawings, assembly instructions, and maintenance manuals.
1.3.5. Use of AutoCAD in Interior Design
AutoCAD has become a staple in the field of interior design, empowering professionals to visualize and communicate their design concepts effectively. Interior designers use AutoCAD to create detailed floor plans, elevations, and 3D models of interior spaces. The software’s extensive library of furniture, fixtures, and materials allows designers to accurately represent their design intent.
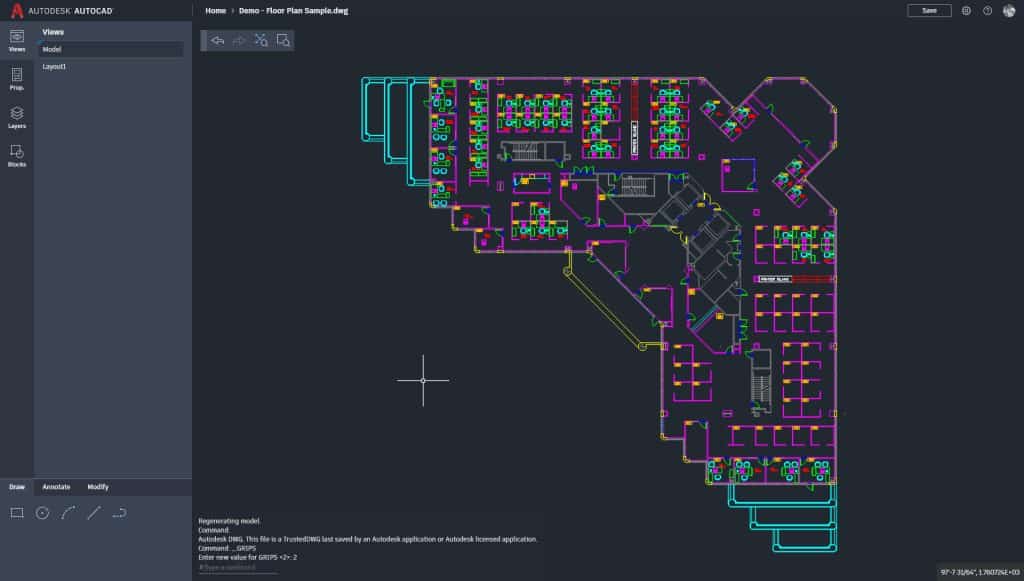
AutoCAD’s rendering capabilities enable designers to apply realistic textures, lighting, and materials to their models, helping clients visualize the final look and feel of the space. Furthermore, AutoCAD’s annotation tools aid in the creation of construction documents, including detailed specifications and material schedules.
By understanding the significance of AutoCAD in various industries, we can appreciate its versatility and the positive impact it has on professionals across different domains. In the following chapters, we will delve deeper into AutoCAD’s features and functionalities, providing you with the knowledge and skills to excel in using this powerful design software.
1.4: Comparison with Other CAD Software
1.4.1 AutoCAD vs. SolidWorks

1.4.1.1 Similarities Between AutoCAD and SolidWorks
Both AutoCAD and SolidWorks are popular CAD software programs used extensively in the engineering and design fields. They share several similarities, including:
- 2D Drafting: Both AutoCAD and SolidWorks support 2D drafting, allowing users to create precise technical drawings and documentation.
- Industry Standards: Both software programs adhere to industry standards and are widely recognized and used by professionals across various industries.
- Geometry Creation: AutoCAD and SolidWorks provide tools for creating and modifying geometric shapes, lines, and curves.
- Parametric Modeling: Both software programs support parametric modeling, enabling users to create models that can be easily modified by changing parameters.
1.4.1.2 Differences in Design Capabilities
While AutoCAD and SolidWorks share some similarities, they also have notable differences in their design capabilities:
- 3D Modeling: SolidWorks is primarily focused on 3D modeling and provides a comprehensive set of tools specifically designed for creating complex 3D models, assemblies, and simulations. AutoCAD, on the other hand, offers 3D modeling capabilities but is generally considered more suitable for 2D drafting.
- Assembly Design: SolidWorks offers robust features for creating and managing assemblies, including mechanisms, mates, and interference detection. AutoCAD, although it has some assembly tools, does not provide the same level of functionality and ease of use for complex assembly design.
1.4.1.3 User Interface Comparison
The user interfaces of AutoCAD and SolidWorks differ in terms of their layout and functionality:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD has a command-line interface combined with a graphical user interface (GUI). It relies heavily on keyboard shortcuts and commands, which can be efficient for experienced users but may have a steeper learning curve for beginners.
- SolidWorks: SolidWorks has a more intuitive and visually-oriented interface. It utilizes toolbars, context menus, and a feature tree to provide easy access to various design tools and features. SolidWorks’ interface is generally considered more user-friendly, especially for those new to CAD software.
1.4.1.4 Pricing and Value
When considering pricing and value, it’s important to note that AutoCAD and SolidWorks are different in terms of their pricing models and target markets:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD is available as a subscription-based software, offering various pricing plans tailored to different user requirements. It is widely used in industries such as architecture, construction, and manufacturing, making it a versatile choice for professionals who require both 2D drafting and 3D modeling capabilities.
- SolidWorks: SolidWorks follows a similar subscription-based pricing model. It is specifically designed for mechanical and product design, focusing heavily on 3D modeling and simulation capabilities. SolidWorks is widely used in industries such as engineering, automotive, and aerospace.
1.4.2 AutoCAD vs. Revit

1.4.2.1 Similarities Between AutoCAD and Revit
AutoCAD and Revit, both developed by Autodesk, share certain similarities due to their common origin:
- Autodesk Platform: AutoCAD and Revit are part of the Autodesk software family, benefiting from interoperability and compatibility with other Autodesk products.
- 3D Modeling: Both AutoCAD and Revit support 3D modeling capabilities, allowing users to create detailed 3D models of buildings and structures.
- File Formats: AutoCAD and Revit can work with various file formats commonly used in the CAD industry, such as DWG and DXF.
1.4.2.2 Differences in BIM Capabilities
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a key differentiator between AutoCAD and Revit:
- AutoCAD: While AutoCAD offers some BIM features, it is primarily known for its 2D drafting capabilities. It lacks the comprehensive set of tools specifically tailored for BIM workflows that Revit provides.
- Revit: Revit is a dedicated BIM software that focuses on the entire building lifecycle. It includes advanced features for architectural design, structural engineering, MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems, and collaboration. Revit’s BIM capabilities allow for intelligent and coordinated designs, facilitating better coordination between disciplines and reducing errors.
1.4.2.3 User Interface Comparison
The user interfaces of AutoCAD and Revit have similarities but also some notable differences:
- AutoCAD: As mentioned earlier, AutoCAD employs a command-line interface along with a graphical user interface (GUI). The command line provides precise control and flexibility, while the GUI offers a range of visual tools and features.
- Revit: Revit has a more specialized interface that is optimized for BIM workflows. It provides dedicated panels and tools for creating building elements, managing parameters, and accessing BIM-specific features. Revit’s interface is designed to enhance collaboration and streamline the design process within the context of building projects.
1.4.2.4 Pricing and Value
AutoCAD and Revit differ in terms of their pricing models and target markets:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD’s pricing structure caters to a broader user base, including professionals from various industries. Its subscription plans offer flexibility and different feature sets, making it suitable for both 2D drafting and basic 3D modeling needs.
- Revit: Revit’s pricing is geared towards the architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. It is specifically designed for BIM workflows, providing advanced tools and features for building professionals. Revit’s focus on BIM makes it an indispensable software for those involved in architectural design and building projects.
1.4.3 AutoCAD vs. SketchUp
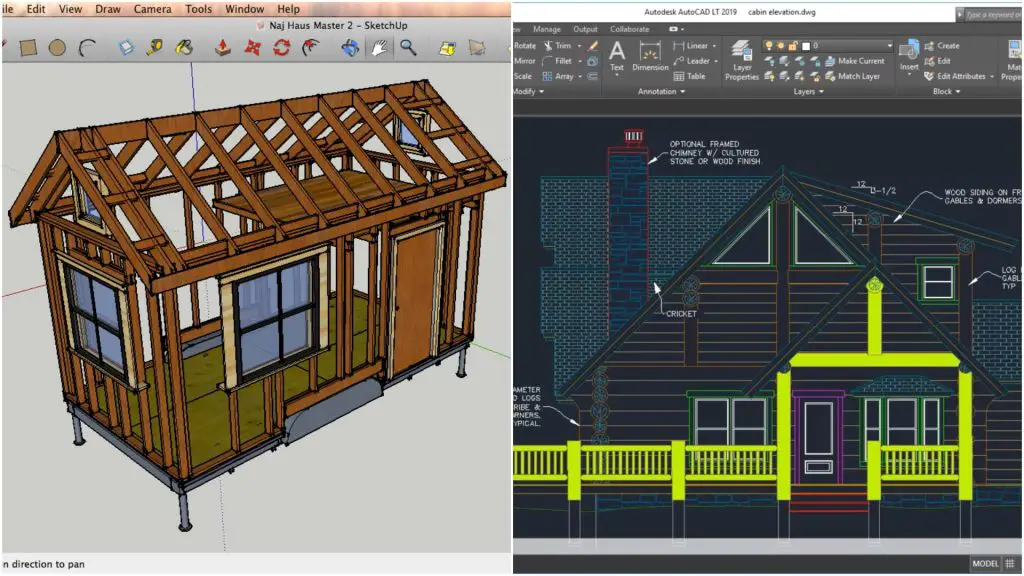
1.4.3.1 Similarities Between AutoCAD and SketchUp
AutoCAD and SketchUp have some similarities, especially in terms of their general purpose as CAD tools:
- 3D Modeling: Both AutoCAD and SketchUp support 3D modeling, allowing users to create 3D representations of objects, buildings, and landscapes.
- Integration with Other Software: Both software programs offer integrations with other tools and file formats, allowing users to exchange data and collaborate with other software platforms.
- Industry Adoption: AutoCAD and SketchUp are widely adopted in the architecture, design, and construction industries, making them popular choices among professionals.
1.4.3.2 Differences in 3D Modeling Capabilities
Although AutoCAD and SketchUp share some common ground, they differ in their approach to 3D modeling:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD provides a wide range of 3D modeling tools, enabling users to create complex 3D designs. It focuses on precision and technical documentation, making it suitable for industries such as engineering and manufacturing.
- SketchUp: SketchUp emphasizes ease of use and quick concept modeling. It offers a streamlined 3D modeling environment with intuitive tools that facilitate fast creation of 3D shapes and objects. SketchUp’s strength lies in its simplicity and flexibility, making it popular among architects and designers.
1.4.3.3 User Interface Comparison
The user interfaces of AutoCAD and SketchUp have their own unique characteristics:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD utilizes a command-line interface combined with a graphical user interface (GUI). The command line allows for precise control and efficiency, while the GUI offers a comprehensive set of tools and features. AutoCAD’s interface may have a steeper learning curve due to its extensive functionality.
- SketchUp: SketchUp features a user-friendly interface with a simplified toolbar and intuitive controls. It focuses on visual interactions and provides a straightforward modeling environment. SketchUp’s interface is designed to be accessible to beginners and experienced users alike.
1.4.3.4 Pricing and Value
AutoCAD and SketchUp differ in terms of their pricing and target markets:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD offers flexible subscription plans catering to various user needs. Its pricing reflects its wide range of functionalities, making it a valuable choice for professionals requiring extensive 2D drafting and 3D modeling capabilities.
- SketchUp: SketchUp offers different pricing tiers, including a free version with limited functionality. It is positioned as a more affordable and accessible option, particularly for architectural and design enthusiasts who need a tool for quick concept modeling and visualization.
Conclusion
As we conclude this first module, it’s clear that AutoCAD, from its inception to the latest versions, has been a cornerstone in the realm of Computer-Aided Design. Its innovative and versatile features have been instrumental in propelling industries forward, offering an efficient and reliable platform for designers, engineers, and professionals across diverse fields. Through the exploration of its history, application, and comparison with other CAD software, we’ve gained a profound understanding of the irreplaceable role AutoCAD plays in shaping our physical world. As technology continues to evolve and expand, we can anticipate that AutoCAD’s influence will persist, affirming its place as an indispensable tool in the design and engineering industries.